As the economy recovered from the COVID-19 pandemic, inflation spiked sharply. The Federal Reserve started raising the target range for the federal funds rate, from near zero to more than 5% in less than 18 months, with the goal of helping to contain rising inflation. Investors who were holding bonds at low interest rates faced difficulties as a result of this sudden spike in rates. When interest rates rise, bond prices drop. The inverse is also true as seen in the picture below.
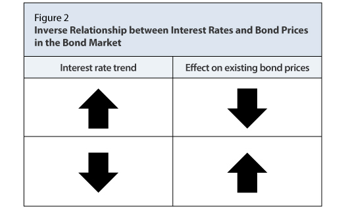
Source: research.stlouisfed.org
Since its start in March 2022, the Federal Reserve’s rate-hike cycle has driven interest rates to levels not seen since 2007. This can be detrimental to those who need to borrow money for expensive things like vehicles, university education, or housing.
This is due to the fact that rate-hike cycles, may eventually bring an economy that is too strong to the verge of being too weak.
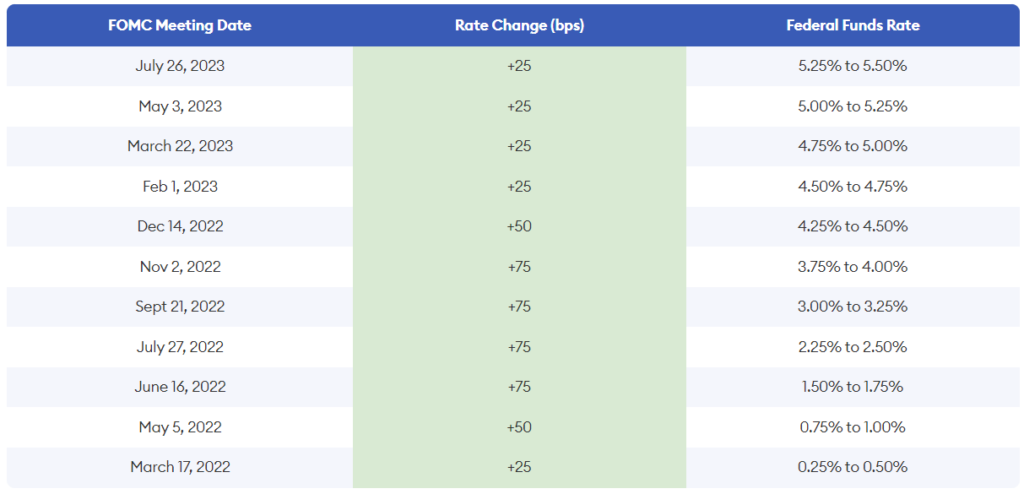
Source: https://www.forbes.com/advisor/investing/fed-funds-rate-history/
How does this affect you?
Changes in interest rates can have different effects on an individual based on their unique financial situation and personal preferences. Here are a few broad things you should think about:
1. Cost of Borrowing:
- Mortgages and Loans: A rise in interest rates usually impacts mortgage and loan interest rates, hence increasing the cost of borrowing for individuals. You are essentially paying more every month on your mortgage. The bigger the loan, the greater the impact.
2. Investments and Savings:
- Savings Accounts: Those who save money may benefit from increased interest rates since they can earn more on their fixed-income investments and savings accounts. Lower rates, on the other hand, can lead to smaller returns on savings – just as what we’ve observed in the decade prior to 2022.
- Investment Portfolios: The value of holdings in your investment portfolio may fluctuate. For example, the performance of equities and bonds may be impacted by increasing interest rates.
3. Consumer Spending:
- Pressure on business loans: Rents hike and shop owners have to charge more to make their economics possible. Consumers have to spend more for the same goods.
4. Housing Market:
- Homebuyers: As mortgage rates rise, it drives up the cost of buying a property. This may affect affordability for potential buyers. Loan eligibility becomes tougher.
- Homeowners: Current homeowners with floating-rate mortgages may experience an increase in their monthly payments.
5. Employment and Economic Growth:
- Interest rate fluctuations can affect the state of the economy, which in turn affects the dynamics of the labour market. Higher rates could have an effect on job creation by slowing down economic development.
6. Currency Impact:
- Travel and Imported products: Variations in exchange rates brought on by discrepancies in interest rates may have an effect on the price of imported products and travel. The purchasing power of an individual might be impacted by a stronger or weaker home currency.
7. Retirement Planning:
- Pension and Retirement Accounts: Interest rate fluctuations may have an impact on retirees and those making retirement plans. Interest rates, for example, may have an effect on the income from fixed-income investments, which are often included in retirement portfolios.
In addition, the impact on the common person can be multi-faceted and interconnected. Personal financial situations, debt levels, investment strategies, and employment status, play a significant role in how individuals are affected by changes in interest rates.
Here are ways you can manage:
- Review and Adjust Debt:
- Pay Down High-Interest Debt: Prioritize paying down high-interest debt, such as credit card balances. This can help mitigate the impact of rising interest rates on borrowing costs.
- Diversify and Manage Investments:
- Diversification: Diversify investment portfolios to spread risk across different asset classes. This can help mitigate the impact of interest rate changes on specific investments. For example, long-maturity bonds are particularly more sensitive and vulnerable to shifts in interest rates.
- Manage: You should consider rebalancing and adjust your investment allocation to manage interest rate risk.
- Evaluate Savings and Emergency Funds:
- Emergency Fund: Maintain an emergency fund with enough savings to cover three to six months’ worth of living expenses. This can provide a financial cushion during periods of economic uncertainty.
- Savings Accounts: Explore high-yield savings accounts or other low-risk investment options that offer better returns than traditional savings accounts.
- Adjust Spending Habits:
- Budgeting: Adhere to your budget and control spending. This can help you to save more and reduce reliance on credit during challenging times.
- Emergency Preparedness: Be prepared for unexpected financial challenges by having contingency plans in place. This may include identifying areas where expenses can be cut if needed.
- Evaluate and Plan for Major Purchases:
- Timing Major Purchases: Where possible, time major purchases (such as a home or car) when interest rates are favourable. This can lead to lower borrowing costs.
- Stay Informed and Plan Ahead:
- Economic Awareness: Stay informed about economic conditions and interest rate trends. Being aware of potential changes allows you to plan ahead and make informed financial decisions.
The effects of interest rates on the market and the economy should not be overlooked. Management of your investment portfolio requires thoughtful planning, proper execution and a regular review. Ultimately, investment planning should be a proactive and not a reactive process.
Consider working with financial advisers to develop a comprehensive financial plan for you that accounts for interest rate changes and other economic factors.
At the point of writing, the Fed does not seem to be in a hurry to lower interest rates for fear of re-igniting inflation.

